IBM® SPSS® Amos™ 28
This window allows you to associate observed categorical responses with intervals along a hypothesized underlying numeric scale. You can specify how many intervals there are, and which interval gives rise to which response. You can optionally specify the values of boundaries between intervals. You can also specify that some categorical responses are unordered and should be treated as missing values.
Two examples will be presented here, followed by further explanation.
Example 1
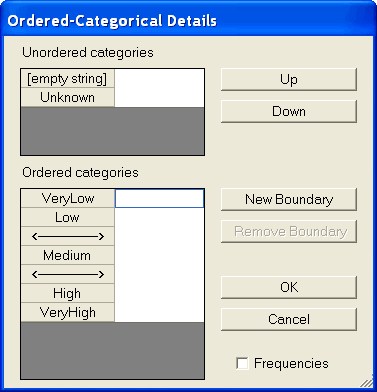
In the following example, there are six distinct responses coded in the data file as VeryLow, Low, Medium, High, VeryHigh and Unknown. In addition, the data file contains empty strings. The empty string is treated as a seventh response category in this window.
The response Unknown and the empty string have been placed in the Unordered categories list. Responses in the Unordered categories list are treated as missing. They give no information about the value of the underlying numeric variable.
There are two boundaries represented by "<-------->" that divide the hypothesized continuous numeric scale into three intervals. An observed response of VeryLow or Low means that the underlying numeric value is in the lowest interval (the one below the lowest boundary.) A response of Medium means that the underlying numeric value is in the middle interval (the one between the two boundaries). A response of High or VeryHigh means that the underlying numeric value is in the highest interval (the interval above the highest boundary).
Notice that no value is assigned to the two category boundaries. Amos will choose values for the boundaries. (See How to choose category boundaries.)
Example 2
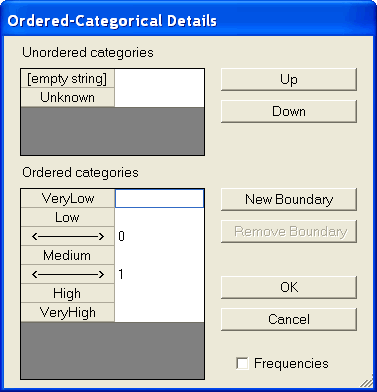
The following example is identical to the previous one, except that the lower boundary is fixed at 0 and the upper boundary is fixed at 1. (You can enter a value for a boundary by first clicking on the boundary and then using the keyboard to enter its value.)
Notes
You can use the buttons at the right side of the window to re-order the categories and the boundaries, and to add and remove boundaries. You can also use drag and drop, but drag and drop only works within the Ordered categories list and within the Unordered categories list, and you must initiate the dragging operation within the gray area of the list. You can't drag from one list to the other.
Use the Up and Down buttons to move a response from one list to the other.